Fundamentals of Physical Geography
Chapter 4: Distribution of Oceans and Continents
Q1. What do you mean by continental drift?
Q2. Discuss about the evidences in support of the continental drift.
Q3. Write a short note on tillite formation.
Q4. Explain about the forces responsible for continental drift as suggested by Alfred Wegener.
Q5. What are the evidences proves that ocean floor is spreading?
Q6. Discuss about plate techtonic theory with diagram.
Q7. Briefly explain about the zone of subduction with diagram.
Q. 1 What are the evidences in support of the continental drift theory?
Answer: -
Wegner gave followings evidences in support of the continental drift: -
1) The Matching of Continents (Jig-Saw-Fit): - The shorelines of Africa and South America facing each other have a remarkable and unmistakable match.
2) Rocks of Same Age Across the Oceans: - The belt of ancient rocks of 2,000 million years from Brazil coast matches with those from western Africa. The earliest marine deposits along the coastline of South America and Africa are of the Jurassic age. This suggests that the ocean did not exist prior to that time.
3) Tillite: - It is the sedimentary rock formed out of deposits of glaciers. The tillite is found in all the broken parts of Gondwanaland. This shows that all the southern continents had similar histories.
4) Placer Deposits: - The occurrence of rich placer deposits of gold and the absolute absence of source rock in the Ghana coast accurately matches with same deposits in Brazil. This shows that these gold deposits of the Ghana are derived from the Brazil Plateau when the two continents move side by side.
5) Distribution of Fossils: - The distribution of fossils shows that same species of plants and animals were found in different parts of the Gondwanaland.
Q. 2 What were the forces suggested by Wegener for the movement of the continents?
Answer: -
1) Pole-Fleeing Force: - The polar-fleeing force relates to the rotation of the Earth. The Earth is not a perfect sphere; it has a bulge at the equator. This bulge is due to the rotation of the Earth.
2) Tidal Force: - The tidal force is due to the attraction of the moon and the sun that develops tides in oceanic waters. Wegener believed that these forces would become effective when applied over many million years.
Q. 3 Give the configuration of Ocean Floor. Or
The ocean floor may be segmented into how many divisions based on the depth as well as the forms of relief?
Or
What were the major post-drift discoveries that rejuvenated the interest of scientists in the study of distribution of oceans and continents?
Answer: -
A number of discoveries during the post-war period added new information to geological literature. Mainly, the information collected from the ocean floor mapping provided new dimensions for the study of distribution of oceans and continents.
1) Convectional Current Theory: - Arthur Holmes, in 1930s, argued that a system of convectional currents exists in the entire mantle portion. These currents are generated due to radioactive elements causing thermal differences in the mantle portion. This was an attempt to provide an explanation to the issue of force, on the basis of which contemporary scientists discarded the continental drift theory.
2) Mapping of the Ocean Floor: - Detailed research of the ocean configuration revealed that the ocean floor is not just a vast plain but it is full of relief.
3) Ocean Floor Configuration: - Expeditions to map the oceanic floor in the post-war period provided a detailed picture of the ocean relief and indicated the existence of submerged mountain ranges as well as deep trenches, mostly located closer to the continent margins.
4) Continental Margins: - The dating of the rocks from the oceanic crust revealed the fact that they are much younger than the continental areas.
5) Abyssal Plains: - These are extensive plains that lie between the continental margins and mid-oceanic ridges. The abyssal plains are the areas where the continental sediments that move beyond the margins get deposited.
6) The mid-oceanic ridges: - The Mid Oceanic Ridges were found to be most active in terms of volcanic eruptions. It is the longest mountain-chain on the surface of the Earth though submerged under the oceanic waters. Rocks on either side of the crest of oceanic ridges were found to have remarkable similarities both in terms of their constituents and their age.
Q. 4 Explain important theories associated with the movement of continents.
Or
Explain the hypothesis, known as the “Sea-floor Spreading”
Answer: -
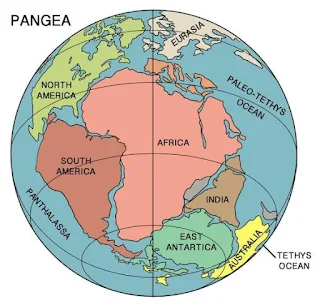
1) Continental Drift: - Abraham Ortelius a Dutch map maker in 1596 first proposed the possibility of joining the continents such as America with Europe and Africa. Antonio ‘Pellegrini’ drew a map showing the three continents together. Alfred Wegener, a German meteorologist put forth the continental drift theory. According to him, all continents formed a single continental mass called Pangaea. All oceans formed a single universal ocean called ‘Panthalassa’ around 200 million years ago. The Pangaea began to split into two large continental masses called Laurasia and Gondwanaland. By further splitting Laurasia formed northern continents and Gondwanaland formed southern continents.
2) Convectional Current Theory: - Check above
3) Sea Floor Spreading: - The ‘Seafloor Spreading’ hypothesis was proposed by the American geophysicist Harry H. Hess in 1960, on the basis of American oceanic cartographer Marie Tharp’s efforts (of creating the first of several maps that revealed the presence of an underwater mountain range) and other new discoveries about the deep-ocean floor. Hess argued that constant eruptions at the crest (top) of oceanic ridges cause the split apart of the oceanic crust and creates a gap between them. This gap is filled by volcanic activity to form a new oceanic crust. The ocean floor thus spreads. To prove his theory Hess gave given evidences i.e.
a) The younger age of the oceanic crust.
b) The spreading of one ocean does not cause the shrinking of the other.
4) Plate Tectonics: - It was in 1967, McKenzie and Parker and also Morgan, independently collected the available ideas and came out with another concept termed as Plate Tectonics. The theory of plate tectonics proposes that the Earth’s lithosphere is divided into seven major and some minor plates. These plates have been constantly moving over the globe throughout the history of the Earth.
It is not the continent that moves as believed by Wegener. Continents are part of a plate and what moves is the plate. All the plates have moved in the geological past, and shall continue to move in the future as well.
Q. 5 Explain the distribution of Earthquake and volcanic plate on the Earth.
Answer: -
1) It starts from Atlantic Ocean almost parallel to the coastlines. It further extends into the Indian Ocean. It bifurcates a little south of the Indian subcontinent with one branch moving into East Africa and the other meeting a similar line from Myanmar to New Guiana.
2) Another area of concentration is the Alpine-Himalayan system and the rim of the Pacific Ocean.
3) In general, the focus of the Earthquake in the areas of mid-oceanic ridge is at shallow depths whereas it is deeper along the Alpine-Himalayan belt and the rim of the Pacific.
4) The map of volcanoes also shows a similar pattern. The rim of the Pacific is also called rim of fire due to the existence of active volcanoes in this area.
Q. 6 What information do we get from the mapping of the ocean floor and paleomagnetic studies of rocks from oceanic regions?
Answer: -
1) It was realised that all along the mid- oceanic ridges, volcanic eruptions are common and they bring huge amounts of lava to the surface in this area.
2) The rocks found on either sides of the crest of mid-oceanic ridges show remarkable similarities in terms of period of formation, chemical compositions and magnetic properties.
3) The ocean crust rocks are much younger than the continental rocks. The age of rocks in the oceanic crust is not more than 200 million years old anywhere. Some of the continental rock formations are as old as 3,200 million years.
4) The sediments on the ocean floor are very thin. Scientists expected that if the ocean floors were as old as the continent, to have a complete sequence of
sediments for a period of much longer duration. However, the sediment column was not found anywhere to be older than 200 million years.
5) The deep trenches have deep-seated Earthquake occurrences while in the mid-oceanic ridge areas, the quake focus have shallow’ depths.
Q. 7 According to tectonic plates theory in how many plates has the Earth been divided? Explain.
Answer: -
The theory of plate tectonics proposes that the Earth’s lithosphere is divided into seven major and some minor plates. The major plates are as follows: -
1) Antarctica and the surrounding oceanic plate.
2) North American plate.
3) South American plate.
4) Pacific plate.
5) India-Australia-New Zealand plate.
6) Africa with the eastern Atlantic floor plate.
7) Eurasia and the adjacent oceanic plate.
Some important minor plates are: -
1) Cocos plate: - It is between Central America and Pacific plate.
2) Nazca plate: - It is between South America and Pacific plate.
3) Arabian plate: - It includes mostly the Saudi Arabian landmass.
4) Philippine plate: - It is between the Asiatic and Pacific plate.
5) Caroline plate: - It is between the Philippine and Indian plate (North of New Guinea).
6) Fuji plate: - It includes North-east of Australia.
Pacific plate is largely an oceanic plate whereas the Eurasian plate may be called a continental plate. Plates are not static. Plates may converge or diverge. Plates may break as well.
Q. 8 Explain different types of boundaries that form as a result of tectonic plates.
Or
Explain tectonic plate theory and its working.
Answer: -
According to the theory of ‘Plate Tectonics’ the entire Earth crust is divided into seven major and some minor plates. These plates have been constantly moving over the globe throughout the history of the Earth. A tectonic plate is also called as lithosphere plate. The theory of plate tectonics was introduced by Mckenzie, Parker and, Morgan in 1967.
Three types of boundaries are formed as a result of tectonic plates: -
1) Divergent Boundaries: - When tectonic plates slowly move away from each other this type of movement is called divergent movement and the plates are called divergent plate boundaries. The new crust is formed by volcanic activity. The area where new crust forms is called spreading site.
2) Convergent Boundaries: - When tectonic plates come close to each other this type of movement is called convergent movement and the plates are called convergent plate boundaries. In this movement the crust is destroyed as one plate dived under another. The area where a plate dived is called subduction zone.
3) Transform Boundaries: - When the tectonic plates move horizontally side by side this type of movement is called transform movement and the plates are called transform plate boundaries. In this movement the crust is neither produced nor destroyed.
Q. 9 How are the convectional currents in the mantle initiated and maintained?
Or
On what basis has continent drifting theory been discarded?
Answer: -
Arthur Holmes in 1930s discussed the possibility of convection currents operating in the mantle portion. These currents are generated due to radioactive elements causing thermal differences in the mantle portion.
According to Holmes, there exists a system of such currents in the entire mantle portion. This was an attempt to provide an explanation to the issue of force, on the basis of which contemporary scientists discarded the continental drift theory.
Q. 10 What are the causes of plate movement?
Answer: -
1) Thermal Convection: - Arthur Holmes propose that the idea in 1930 that the convection currents forces the movement of plates these convection currents are generated due to radioactive elements within the Earth.
2) Floating of Plates: - The hard plates of lithosphere which floats on more mobile asthenosphere are in constant motion.
3) Hotspot of Volcanic Activity: - hotspots are places within the mental where rocks melt to generate Magma availability of hotspots increases the volcanic activity the hotspots are also increases the convection currents within the Earth.
4) Volcanic Eruptions: - source of Magma in the metal remains fixed in position while the lithospheric paint above it moves slowly e the volcanoes are formed over hotspot these hotspots affects the convection currents which is a major cause of movement of tectonic plates.
Q. 11 What was the condition of India when Pangaea broke? What was India’s status before that?
Or
What was the location of the Indian landmass during the formation of the Deccan Traps?
Or
Explain the movement in Indian plate.
Answer: -
1) The Indian plate includes Peninsular India and the Australian continental portions.
2) The Tethys Sea separated it from the Asian continent till about 225 million years ago.
3) India is supposed to have started her northward journey about 200 million years ago at the time when Pangaea broke.
4) About 140 million years before the present, the subcontinent was located as south as 50°South Latitude.
5) During the movement of the Indian plate towards the Asiatic plate, a major event that occurred was the outpouring of lava and formation of the Deccan Traps.
6) This started somewhere around 60 million years ago and continued for a long period of time.
7) The subcontinent was still close to the equator.
8) India collided with Asia about 40-50 million years ago causing rapid uplift and the event of formation of the Himalayas took place.
9) Scientists believe that the process is still continuing and the height of the Himalayas is rising even to this date.
Q.1. How do you think the rate of plate movement is determined?
Answer: -
Plates move at rates of about an inch (a few centimeters) per year. Scientists first estimated the rate of plate movement based on radiometric dating of ocean crust. By determining the age of a crustal sample, and knowing its distance from the mid-ocean ridge at which it formed, they estimate the rate of new ocean floor production and plate movement. Today, satellites capable of measurement of plate motion provide a more direct method. Results from these two methods agree fairly closely. The fastest plates move more than 4 in (10 cm) per year. The rate of motion of the North American plate averages 1.2 in (3 cm) per year.





.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
Share your knowledge with others